
Chinese AI startup DeepSeek has rapidly gained attention in the artificial intelligence sector, challenging Western tech companies with its cost-efficient, high-performing models.
However, its rise has sparked concerns worldwide, with multiple governments banning or restricting its use due to security and data privacy issues.
Its growing regulatory challenges could shape the future of global AI competition as DeepSeek continues to gain users.

DeepSeek, developed by Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence and Beijing DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence, is a Chinese AI model that has quickly become the most downloaded app on Apple's App Store.
The company claims that its latest models, DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1, rival leading U.S. AI models, such as OpenAI's ChatGPT, at a fraction of the cost.
However, DeepSeek's rapid growth has raised concerns, particularly regarding its data handling practices.
This has led to fears that DeepSeek could be used for data collection by the Chinese government, fueling tensions in the AI race between China and the West.

On Jan. 30, 2025, Italy's Data Protection Authority (Garante) blocked DeepSeek over concerns about how it collects, stores, and processes personal data.
The authority requested detailed information from DeepSeek regarding what personal data it collects, its sources, its legal basis, and whether data is stored in China. However, DeepSeek's responses did not satisfy regulators, leading to an immediate ban in Italy.
As a result, DeepSeek is no longer available on Apple and Google app stores in Italy. Garante also launched an investigation, emphasizing that the Chinese company's claim that it does not operate in Italy does not exempt it from European Union regulations.

The U.S. has also moved against DeepSeek. On Jan. 26, 2025, the U.S. Navy issued an all-hands memo instructing personnel to avoid using DeepSeek's AI "in any capacity" due to security and ethical concerns.
The Navy's Chief Information Officer warned that the app could expose sensitive information. The U.S. Department of Defense has since started restricting DeepSeek access across its networks after reports that Pentagon employees had connected their work computers to DeepSeek's Chinese servers.
U.S. officials have warned that DeepSeek's data storage policies could allow Chinese authorities access to sensitive information. The model's rapid growth has also unsettled the American tech sector, with leading investors and government advisors calling for vigilance in maintaining the U.S.'s AI leadership.
On Jan. 31, Taiwan's Ministry of Digital Affairs (MODA) banned DeepSeek across all public sector institutions, including government agencies, public schools, state-owned enterprises, and infrastructure projects.
The ministry cited the 2019 "Principles on Restricting the Use of Products That Endanger National Cyber Security," which prohibits ICT products considered a potential national security risk. Taiwan's decision aligns with growing international concerns over Chinese AI models' data handling practices.
Beyond outright bans, regulatory authorities in multiple countries are investigating DeepSeek:

DeepSeek's rise has sparked debates not only about AI security but also about the competition between China and the West in artificial intelligence development.
The company's cost-efficient AI models have disrupted financial markets, causing tech giants like Nvidia and Broadcom to lose billions in market value. Investors are increasingly concerned that DeepSeek's ability to develop powerful AI models at lower costs could upend the existing AI hierarchy.
The U.S. government, under President Donald Trump, has already signaled its intent to counter China's AI advancements. The administration recently announced "Stargate," a joint venture between OpenAI, Oracle, and SoftBank aimed at accelerating AI infrastructure investments in the U.S.
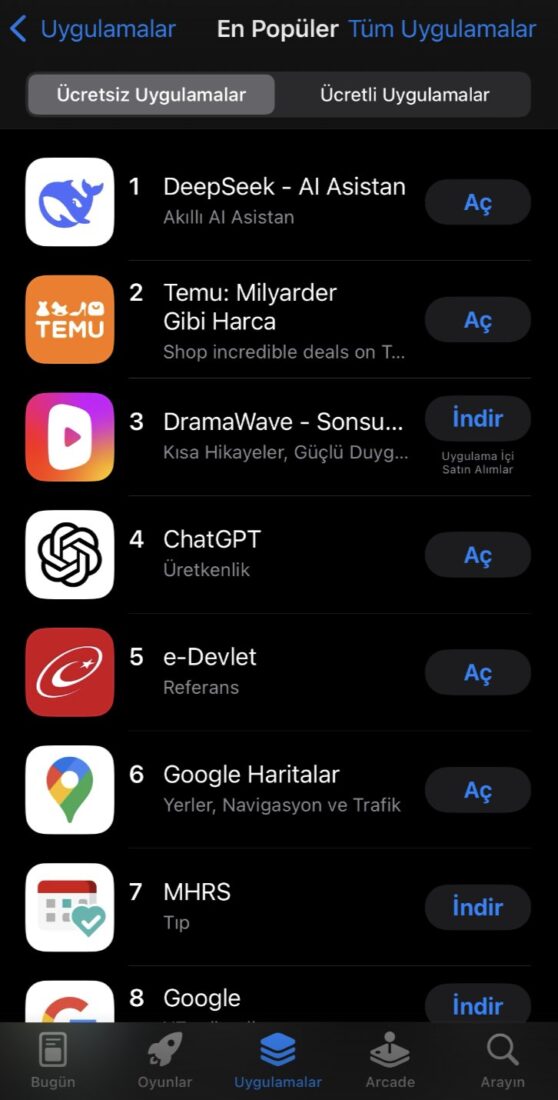
Despite mounting bans and regulatory scrutiny, DeepSeek continues to attract users, particularly in countries where it remains unrestricted.
Its ability to rival Western AI models at significantly lower costs has made it an attractive option for developers and enterprises looking for affordable AI solutions.
However, as more countries examine its data practices, DeepSeek’s global expansion could be hindered by legal and regulatory roadblocks. If additional European and North American regulators decide to follow Italy’s lead, DeepSeek may face an uphill battle in securing international trust and market dominance.